Conditions We Treat.
Home > Conditions > Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)
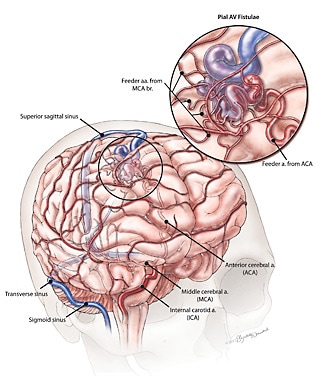
Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM).
An arteriovenous malformation—also known as an AVM—is an abnormal tangle of blood vessels in the brain, which can cause bleeding, seizures or stroke-like symptoms. A brain AVM disrupts the flow of blood from the heart to the brain. The cause of AVMs is unknown.
AVM Symptoms:
Arteriovenous malformation is a rare but serious condition. Though they may occur anywhere in the body, they are most common in the brain and spine. AVMs can cause bleeding in the brain, though a patient might have an AVM with no symptoms. Typical symptoms can include:
- Severe headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- Blurred vision
- Stiff neck
- Loss of consciousness
- Seizures
An AVM might also cause stroke-like symptoms such as paralysis, weakness, numbness, vision problems, balance or coordination problems and speech difficulties. Typically, a brain AVM is diagnosed using a CT scan, MRI or angiogram.
AVM Treatment:
The treatment of a brain arteriovenous malformation depends on the individual patient. Symptom-causing brain AVMs can be treated after they have caused bleeding, or in some patients, an AVM is found before it has bled and is treated to prevent it from bleeding. Treatment can include surgery, embolization or radiosurgery.
- Surgery for brain AVMs requires opening the skull and surgically removing the AVM from the brain. This treatment is most common for AVMs that are in an area not likely to cause brain bleeding.
- Embolization is a minimally invasive treatment that requires injecting substances into the AVM to block off the abnormal vessels. This is done through a catheter inserted in the groin that is tracked through the body with X-rays.
- Radiosurgery is a one-time treatment of high-focused radiation to the brain AVM. This treatment is common for small AVMs or ones in difficult-to-reach areas of the brain.
The main goal of AVM treatment is to prevent bleeding in the brain, which can cause stroke or other brain damage. However, some patients may not need treatment for AVMs and may instead be monitored closely for any signs of bleeding.
*Disclaimer: The materials available at this website are for informational purposes only and not for the purpose of providing medical advice. You should contact your doctor to obtain advice with respect to any particular medical issue or problem. Use and access to this website or any of the links contained within the site do not create a doctor-client relationship. The opinions expressed at or through this site are the opinions of the individual author and may not reflect the opinions of the medical office or any individual doctor or physician.
We specialize in AVM Treatment.
At Nashville Neurosurgery Associates, we are proud to be one of the region’s leading neurosurgical centers. Our endovascular team are experts in the care and treatment of arteriovenous malformations.